Common types of bearing materials used in Vertical Turbine Pumps, their properties & limitations

Common types of bearing materials used in Vertical Turbine Pumps, their properties & limitations
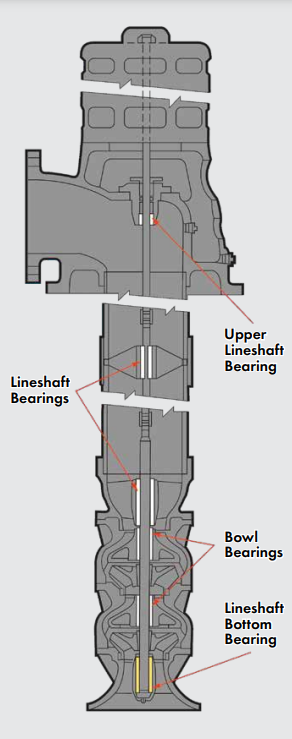
There are several common types of bearing materials used in Vertical Turbine Pumps (VTP), including bronze, rubber, carbon graphite, Teflon, thermoset laminates, and thermoplastics. Each material has its own set of properties and limitations:
- Bronze: This is the most popular bearing material used in VTPs because it is readily available and easy to machine and install. However, bronze has poor abrasion resistance and can deform under impact, which can increase shaft clearances. Bronze also requires oil or grease for lubrication, which can contaminate the pumped water. Most bronze bearings are not approved for drinking water due to their lead content, and they can be expensive in large sizes.
- Rubber: Rubber offers good abrasion resistance and can accept some vibration and shock loading. However, it is too soft to install directly into a pump housing and requires a metallic or phenolic carrier. Rubber has a high coefficient of friction, which makes dry starts not recommended. Some manufacturers try to address this issue by applying a thin layer of Teflon to the bearing ID. Rubber has lower mechanical strength, so longer bearing lengths are recommended to allow for faster cooling and longer life. Rebuilding a pump with rubber bearings is difficult, as the housing and shaft usually require non-standard sizes.
- Carbon graphite: This material has good dry running capabilities and temperature resistance, but it offers poor abrasion resistance and is brittle, which can cause fractures during installation or thermal shock.
- Teflon: Teflon bearings have excellent dry run capabilities and chemical strength but poor abrasion resistance. Due to its low mechanical strength, Teflon bearings cannot be retained by traditional press-fit methods.
- Thermoset laminate: This material is low cost, but physical properties can vary depending on the manufacturer. Most thermoset laminates are made with cotton or glass cloth layers impregnated with thermosetting resins. They offer poor abrasion resistance and dry run capabilities, but some manufacturers try to enhance dry running capabilities by applying a thin layer of Teflon to the wear surface. Machining thermoset laminates can pose health issues due to fine resin dust being generated during the process, and surface cords can become exposed, leading to significant surface swell and reduced running clearance.
- Thermoplastics: There are many manufacturers of thermoplastic materials, with different materials offering varying properties. Nylon thermoplastics have high moisture absorption and poor abrasion resistance, while acetal has worse abrasion resistance and poor impact resistance. Some thermoplastics offer good abrasion resistance, such as PPS (Ryton), which has good chemical resistance but is brittle and can crack due to shock or vibration. Engineered thermoplastics like Vespel and PEEK are overkill for water-lubricated pumps, but are more appropriate for harsh chemical or high temperature applications. PEEK has high temperature capabilities and good chemical and steam resistance, but is expensive and has poor abrasion resistance.
Do you have expensive challenges with your bearings and need a creative, cost-effective solution? Allow Millstream Engineering’s team of specialists to lead your group to a successful, economical solution. Contact us today.

