Preventing Wear in Self-Lubricated Bearings During Oscillating Motion

Preventing Wear in Self-Lubricated Bearings During Oscillating Motion
In applications involving oscillating motion—such as pivot bearings, roller wheel bushings, Pillow block bearings, and linkage bushings—self-lubricated bearings are essential for reducing maintenance and preventing contamination. However, the repetitive back-and-forth movement can lead to wear over time. Thordon Bearings offers advanced polymer bearing solutions designed to address these challenges effectively.
1. Advanced Polymer Bearing Materials
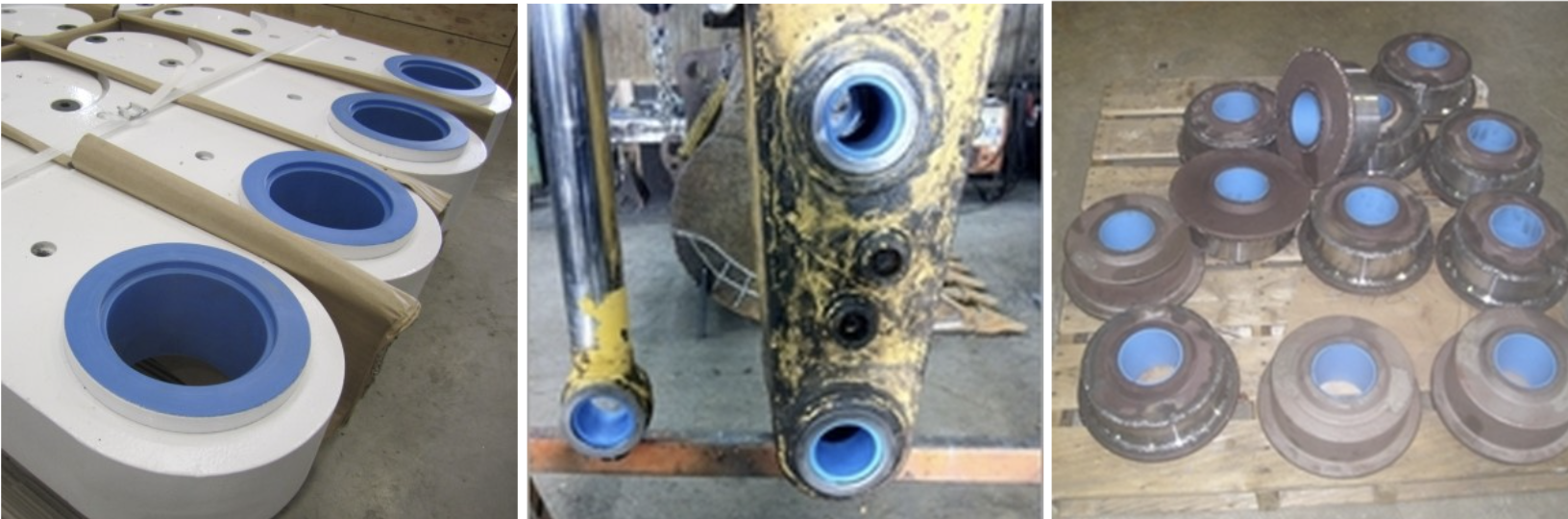

Thordon’s polymer bearings, such as ThorPlas-Blue, are engineered to withstand high pressures up to 45 MPa (6,527 psi) and are self-lubricating, eliminating the need for external lubrication. These materials exhibit low friction and wear rates, making them ideal for oscillating applications. Their homogeneous structure ensures consistent performance throughout the bearing’s life.
2. Surface Finish and Hardness
The surface finish of the mating shaft significantly impacts bearing performance. A smoother surface reduces friction and wear, as rough surfaces can abrade the bearing material more quickly. Ensuring that the shaft material has adequate hardness prevents premature wear of the mating surface. Surface treatments like hard chrome plating or nitriding can enhance hardness and wear resistance.
3. Proper Load Distribution and Alignment
Misalignment and uneven load distribution can accelerate wear in oscillating applications. Ensuring that the bearing is properly aligned and that loads are evenly distributed across the bearing surface reduces stress concentrations. Design considerations, such as using spherical bearings or incorporating alignment features, can help accommodate misalignment and maintain optimal contact conditions.
4. Control of Oscillation Parameters
The amplitude and frequency of oscillation affect wear rates. High-frequency or large-angle oscillations can increase the rate of wear due to increased frictional interactions. Where possible, optimizing these parameters within the application’s requirements can reduce wear. Selecting bearings designed specifically for high-frequency or high-angle oscillations can also improve performance.
5. Use of Wiper Seals for Dust and Dirt Exclusion
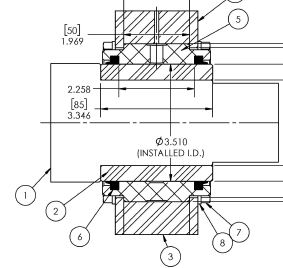
Contaminants like dust, dirt, and debris are significant contributors to wear in bearings. Implementing wiper seals is an effective strategy to prevent external contaminants from entering the bearing interface. Wiper seals act as a physical barrier, scraping off particles from the shaft surface before they can infiltrate the bearing. This exclusion of contaminants minimizes abrasive wear and extends the bearing’s operational life. When selecting wiper seals, consider materials compatible with the operating environment and the bearing materials to ensure effective sealing without introducing additional friction.
6. Environmental Control
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can influence wear rates. Extreme temperatures can degrade bearing materials or alter their mechanical properties. Selecting materials suitable for the operating environment and incorporating protective measures like shields or enclosures can mitigate these effects. In corrosive environments, materials resistant to chemical attack should be used to prevent degradation.
7. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Even though self-lubricated bearings require minimal maintenance, periodic inspections are essential to detect early signs of wear or damage. Monitoring parameters like torque resistance, noise, and vibration can provide insights into the bearing’s condition. Replacing bearings at the first signs of significant wear prevents unexpected failures and extends the equipment’s overall lifespan.

Conclusion
Preventing wear in self-lubricated bearings during oscillating motion involves a holistic approach that includes material selection, design optimization, environmental protection, and regular maintenance. By implementing wiper seals for dust and dirt exclusion, engineers and maintenance professionals can significantly reduce abrasive wear caused by contaminants. Combining these strategies ensures that self-lubricated bearings operate efficiently and reliably, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs in various industrial applications.

